What are the 6 types of hydroponics?
A Comprehensive Guide About Different Types of Hydroponics Systems
Hydroponics is a specialized system of growing food in the nutrient solution than the soil or other growing media. Numerous variations have been developed in this system over the past few years and different types are being used for optimizing production potential according to requirements. There has been significant research in hydroponic production and cultivation, and it has led to a good variety of hydroponic production and cultivation systems. The hydroponic system helps to produce good quality, nutritionally rich, and fresh food despite the soil quality and prevailing climatic conditions of the specific region.
At present Europe is the biggest market of hydroponics and France, Netherlands, Spain, USA, and Asia pacific are top producers. The demand for hydroponic-based food production is growing even more due to global warming, climate change, and industrialization. Hydroponics system has huge potential to achieve sustainable food security across the globe. Moreover, there is less utilization of resources as compared to conventional farming and good quality food can be produced in all regions of the globe. Thereby the financial burden of importing food from other areas will be reduced and poor countries can also generate surplus income by selling good quality food to the developed countries. Therefore this article is focused to discuss different types of hydroponic systems and hydroponic farming types.
Some significant advantages of growing in the hydroponic system are as follows.
- More yield, better quality, and nutrient-rich crops
- The use of soilless media ensures pathogen-free production
- Plant growth, development, and yield potential is independent of soil quality, and prevailing climatic conditions of an area
- Better control and monitoring of plant growth is possible
- Growers can control the nutrient concentration by targeted application of the nutrient solution
- The significant potential of nutrient re-utilization and maximizing the resource recovery
- Minimized risk of diseases and insect pest attack by excellent and oriented control over environmental conditions
Crops and Plants for Hydroponics System
The hydroponic system is fairly helpful to grow a wide range of crops including the following.
Edibles: Herbs, celery, watercress, strawberries, cucumbers, peppers, tomatoes, leaf lettuce, cantaloupe, sage, celery, grapes, basil, kale, tomatoes, blueberries, chives, bell peppers, beans, and spinach.
Houseplants: Spider plant, Chinese evergreen, leopard lily, female dragon, Chinese money plant, peace lily, philodendron, arrowhead vine, and Devil’s ivy.
Flowering plants: Hyacinth, peace lily, carnations, gerbera, chrysanthemums, freesia, daffodils, iris, amaryllis, orchids, petunia, daisies, snapdragon, zinnia, brachycome species, coreopsis species, baby’s breath, marigold, gazania, lavender, phlox, hydrangeas, asters, daily lilies, rex begonias, hoya, peace lilies.
The new scientific technologies and tools have enabled the growers to grow all kinds of plants in the hydroponic system by the provision of the right growth dimensions and management systems. However, the growth potential and production status are greatly dependent on the use of the right measures for each type of growing plant.
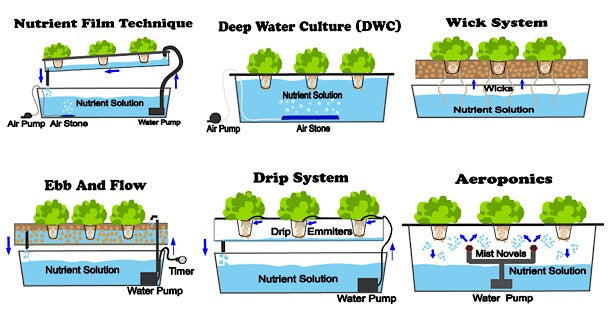
6 Types of Hydroponics
Wick System in Hydroponics

Wick hydroponic system is passive and does not have any moving parts. This system consists of a growing container, reservoir, wicks, growing medium, and aeration system. The growing container is specifically positioned at a shorter distance above the growing reservoir. Wicks are placed in the nutrient solution from the reservoir and are released to the growing medium for the easy absorption and availability of nutrients to the roots of growing plants. The working of this system is based on the capillary action to feed the roots with nutrients. This is a passive system and does not require any moving parts, pumps, and motors for operation. However, this system requires a pump for aerating the nutrient solution and providing oxygen to the plant roots.
Select a container that does not allow the passage of light. This is helpful to restrict the growth of microorganisms and algal bodies. Placing the reservoir in close contact with the growing container helps the wicks efficient delivery of the nutrient solution to the growing medium. Growing mediums having excellent absorption and moisture-holding capacity are ideal choices for the wick hydroponic systems. The most efficient and popular wick system growing media includes vermiculite, perlite, coco coir, and other lightweight structures. Growstones also provide the best wicking capacity, oxygen supply, and moisture to the plants. Strip fabrics, ropes, yarn, and strings can be easily used for the wick system. These materials can be made by using synthetics, polyurethane, nylon, felt, wool, and cotton. Washing these materials before making wicks helps to improve their strength.
Advantages
- This is a simple and easy-to-use hydroponic system.
- Growers can easily scale it up by upcycling and recycling household materials and items.
- Wick system allows low maintenance growing and quality food production throughout the year.
- There is no major requirement for an electricity system.
- It is a sustainable hydroponics system in terms of water use efficiency.
- There is self-regulation of the system and delivery of the nutrient solution is greatly dependent on nutrient consumption by the plants.
Disadvantages
- Growers cannot enjoy a wide range of growing choices.
- The nutrient delivery rate is slower.
- This system can cause a buildup of toxic nutrients, so the replacement of nutrient solutions is a must task. So, it requires rinsing after every 1-2 weeks for better growth.
Deep Water Culture (DWC) or Deep Water Hydroponic System

Deepwater culture is also known as direct water culture where plant roots are continually suspended in highly oxidized, and nutrient-rich water. The other hydroponic systems such as drip systems, aeroponics, and ebb and flow methods are focused on partial water exposure. While deep water culture is focused on the total submission of roots in the water. The use of larger reservoirs is significantly effective to maintain stability in hydroponics farming. Usually, the plants growing in the soil and other growing media cannot tolerate excessive water saturation because it causes suppression in the oxygen levels. However, plants growing in the deep-water culture can easily tolerate water-submerged conditions due to aeration pumps and the constant provision of oxygen. Other than oxygen growers should also constantly provide nutrients, sunlight, optimal temperature, and humidity to maintain the normal growth and development of plants.
Advantages
- This system requires low maintenance after building up.
- It offers extremely fast growth and development than the soil-based growing system.
- This system is provided with some assemblage and moving parts.
Disadvantages
- Deepwater culture requires more care and management for proper maintenance.
- Any mismanagement can cause great fluctuation in the nutrient concentration, water, and soil pH.
- Small scale systems are easy to manage but under calibration or over calibration can cause significant problems in both small scale and large-scale systems.
- Plant roots suffer immediately due to pump failure or power outage for a few minutes only.
- Maintenance of constant water temperature is a difficult task.
Nutrient Film Technique Hydroponics (NFT)

The nutrient film technique is used for growing quick-growing and smaller plants such as baby greens and herbs. Shallow and slightly angled tubes are used in this system for the movement of nutrient solution to the upper portion of the nutrient film system. There is the gradual movement of nutrient solution in the upward direction due to gravity. A tube system provided with the holes is used instead of the growing tray because it allows the easy angle to ensure the proper flow of nutrient solution to the roots. Most of the growers directly plant in these holes and some of the growers use net pots. The plant roots directly fall into the nutrient solution, but roots are not soaked completely in the nutrient solution. In this system, a pump is used to ensure a constant flow of nutrients and oxygen to the plants. This technique is an active hydroponics system due to the involvement of moving parts. This system cannot support the weight of heavy growing plants due to the use of delicate grow media. However, the use of a trellis system is a good choice to support the weight of vining and heavy growing plants.
Advantages
Disadvantages
- Any imbalance in the nutritional composition and nutrient flow can cause stress on growth and root drying.
- The use of saline water is not a good choice for this system and completely effective saline water treatment of wastewater treatment is required for utilization.
- Pump failure or electricity outage can cause the death of growing plants within a few hours only. The situation can get even more severe in the hot weather and warm climatic conditions.
- Vigorously growing roots can cause blockage of system channels.
- Exposure of newly grown plants to intense sunlight can cause fast heating of the channels and roots will become aggregated in the Rockwool.
Ebb and Flow System (Flood and Drain)

Flood and drain system are the most effective and simplest method of hydroponically growing and is an ideal choice for both commercial growers and hobbyists. There is periodic flooding and drainage of nutrient solutions in this system. This system involves two operational phases such as flooding (when the nutrient solution flows through growing areas) and drainage of nutrient solution back to the reservoir. These two actions work simultaneously and thus it is named a flood and drain system. Growers can set up the working of this system in different ways and the growing medium can be filled with solid growth media. It is also possible to leave the grow medium empty and place the plants in the smaller pots in the grow beds.
Most of these systems are provided with inlets, outlets, and two bulkhead fittings. Typically the outlets have customizable heights and inlets are short for controlling the water levels. While there is another variation based on the siphon system where the water pump is running at all times and constantly fills the growing bed. Water can be drained using a siphon after reaching a certain height. Different kinds of siphons are available in the market but bell siphons are being most commonly used. Using automatic drains for this system allows 24/7 running of the pump and eliminates the need for a timer. Different types of growing media work well for different purposes and some examples are stated below.
Improved water retention: Use of Hydroton clay pebbles and lava rock offers maximum retention of nutrients and moisture.
Supporting vegetable roots: Rooting vegetables requires soft growing media for easy movement in the downward direction. Perlite mix, grow mix, vermiculite, and Hydroton are excellent choices to support the best growth of rooted vegetables in the flood and drain system.
Adding buoyancy or weight: The strength of the growing medium is foremost important for holding the weight of water and grow media. There is the filling of grow bed with the water, and it causes floating of growing media that can disrupt the health of plant roots. Therefore, the use of growing media that does not swell and float after the addition of water is greatly important for supporting the best growth.
Advantages
- The use of this system is fairly easy for beginners.
- This system is greatly flexible, and growers have a good choice of using different grow mediums.
- Reusing nutrient solutions makes this system economical and sustainable.
- This system allows roots to dry for some time and supports the development of larger root systems.
- This system easily supports large-scale and commercial production.
Disadvantages
- This system requires more labor and money investment for large-scale setups.
- There is a constant requirement of washing and sterilizing the grow media so this system requires more time, money, and management.
- Removal of damaged and harvested plants can cause problems for the roots of other growing plants.
- Pathogenic contamination in the pot, flood tray, and growing medium can cause contamination of the whole system and shared water sources.
Aeroponic System

The aeroponic system is focused on growing the plants in a specialized environment focused on using mist or air. This system is different from traditional aquaponics and hydroponics as the roots do not grow into any medium but dangle in the air. These plants are periodically fed by misting the water-based nutrient solution on them. However aeroponic systems require a complete enclosure to prevent light contact with the roots and to maintain the humidity. Some aeroponic systems are used in the horizontal direction as the planting beds but tower-based and vertical approaches are also gaining popularity for the space-limited conditions. Mostly the aeroponic systems are being used for growing cucumbers, tomatoes, strawberries, marijuana, and herbs.
Advantages
- This system allows the use of different approaches in one frame.
- It allows fast and massive plant growth.
- The replacement of old plants with new ones is significantly easy.
- There are minimum requirements for maintenance and care.
- This system can be easily supported in space-limited conditions.
- Aeroponics allows easy mobility of plants without affecting their production potential.
- This system supports the development of a healthier and denser rooting system.
- This system can be operated at fairly optimal power supplies.
Disadvantages
- Constant monitoring and care are required for better growth and development of plants.
- The initial setup of aeroponics requires more investment as this system involves automation.
- This system is greatly susceptible to electricity outages.
- Technical knowledge is required for the efficient working of this system.
- The rooting system of the plants growing in the aeroponics requires regular disinfection.
- Long term use and benefits of this system can only be supported by the use of high-pressure systems.
- These systems can produce noise in enclosed environments.
Drip Systems Hydroponics

The drip hydroponic system is focused on delivering the nutrient solution to the plant roots by using drip irrigation. Low flow drip irrigation is significantly effective and minimizes water losses by preventing evaporation. This system can be easily established by using a container for plant roots, a reservoir for holding the nutrient solution, a pond pump, a timer to turn on and off the pump, tubing running from the reservoir pump to the plant roots, and growing media. Growers can easily replace the tubing with drip emitters for easy work. There are two major types of this system such as recovery drip system and non-recovery drip systems also known as recirculating drip systems and non-recirculating drip systems respectively. Recirculating systems are far most efficient for home growers and non-recirculating systems are most commonly used by commercial growers.
Advantages
- This system is simple and easiest to use for year-round growing and production.
- It is also possible to make optimal priced equipment according to the requirements.
- This system does not cause the drying of plant roots in case of a power outage.
- Drip-based hydroponics system is greatly versatile and can be easily used both for small-scale growing and commercial production.
- This system allows great control over the watering schedule, nutrient concentration, and drip location so growers can greatly optimize the production potential according to the requirements.
Disadvantages
- This system is dependent on electricity as compared to the other passive systems.
- Regular monitoring is required to control the fluctuations in the nutrient concentrations and pH levels.
- This system requires more accurate timers than the other systems.
- There is a significant threat of clogging the drip emitters due to nutrient buildup and algal growth.

Leave a comment